Here’s How We Could Brighten Clouds to Cool the Earth
As we confront the tremendous obstacle of local weather improve, we must consider inspiration from even the most not likely sources. Get, for instance, the tens of 1000’s of fossil-fueled ships that chug across the ocean, spewing plumes of pollutants that add to acid rain, ozone depletion, respiratory illnesses, and international warming.
The particles developed by these ship emissions can also generate brighter clouds, which in convert can deliver a cooling impact by way of procedures that come about in a natural way in our environment. What if we could achieve this cooling impact with out at the same time releasing the greenhouse gases and toxic pollutants that ships emit? That is the issue the
Maritime Cloud Brightening (MCB) Project intends to answer.
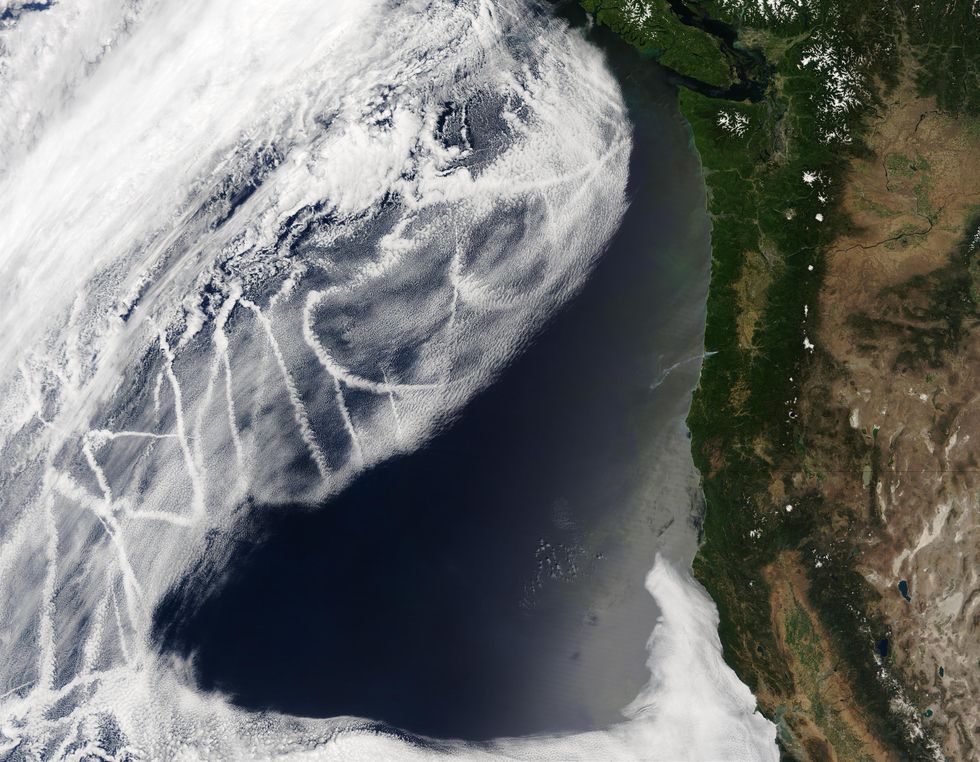
Researchers have acknowledged for many years that the particulate emissions from ships can have a dramatic impact on low-lying stratocumulus clouds previously mentioned the ocean. In satellite photos, components of the Earth’s oceans are streaked with dazzling white strips of clouds that correspond to shipping lanes. These artificially brightened clouds are a consequence of the tiny particles developed by the ships, and they reflect additional daylight back again to house than unperturbed clouds do, and considerably additional than the dim blue ocean underneath. Because these “ship tracks” block some of the sun’s electrical power from reaching Earth’s surface, they stop some of the warming that would normally come about.
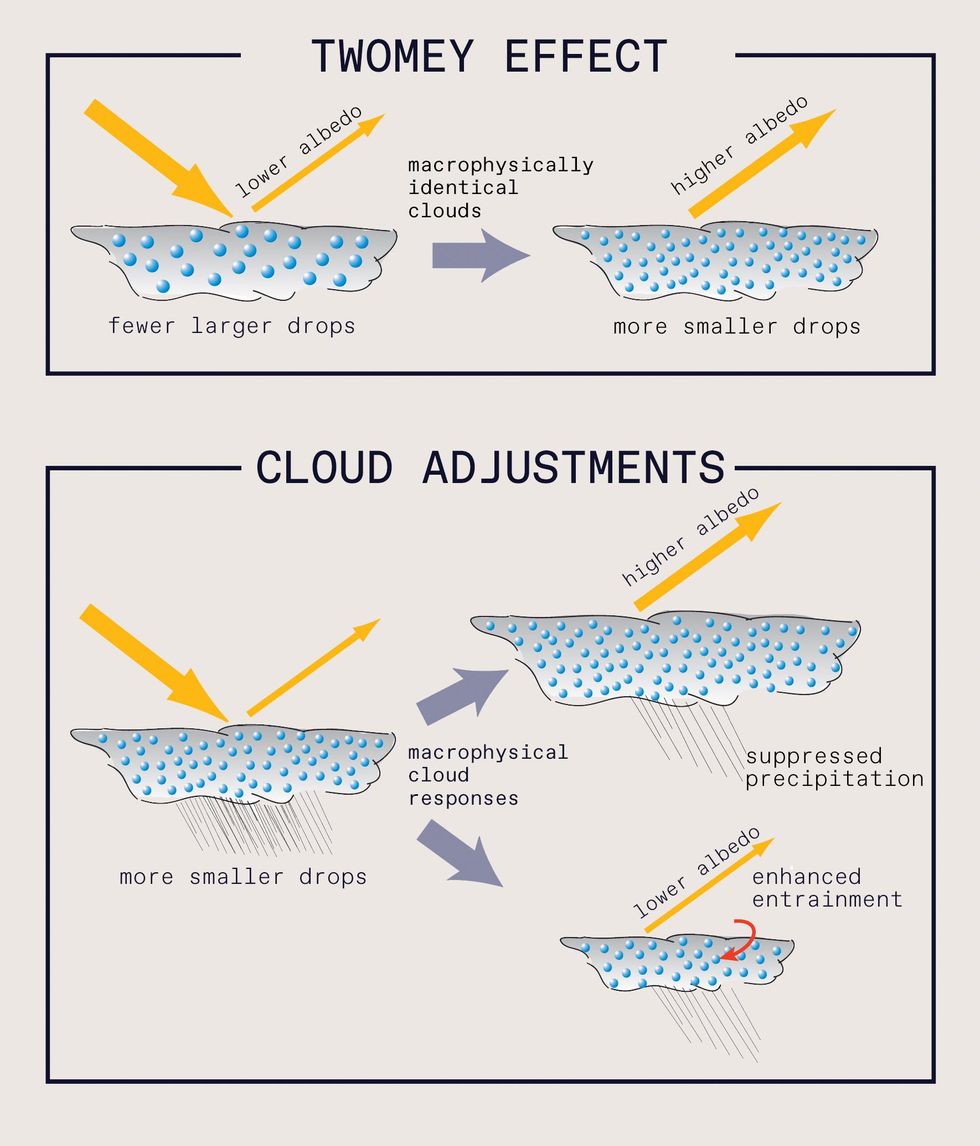
The development of ship tracks is governed by the similar primary rules driving all cloud development. Clouds in a natural way look when the relative humidity exceeds 100 %, initiating condensation in the environment. Individual cloud droplets form all over microscopic particles named cloud condensation nuclei (CCN). Commonly talking, an improve in CCN increases the quantity of cloud droplets even though cutting down their dimension. By way of a phenomenon acknowledged as the
Twomey impact, this significant focus of droplets boosts the clouds’ reflectivity (also named albedo). Sources of CCN consist of aerosols like dust, pollen, soot, and even bacteria, together with person-designed air pollution from factories and ships. In excess of distant components of the ocean, most CCN are of natural origin and consist of sea salt from crashing ocean waves.
Satellite imagery displays “ship tracks” around the ocean: dazzling clouds that form since of particles spewed out by ships.Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Speedy Response Group/GSFC/NASA
The intention of the MCB Project is to look at no matter if deliberately incorporating additional sea salt CCN to low marine clouds would neat the planet. The CCN would be created by spraying seawater from ships. We be expecting that the sprayed seawater would instantaneously dry in the air and form tiny particles of salt, which would rise to the cloud layer by way of convection and act as seeds for cloud droplets. These created particles would be considerably smaller than the particles from crashing waves, so there would be only a smaller relative improve in sea salt mass in the environment. The intention would be to deliver clouds that are a bit brighter (by 5 to 10 %) and perhaps for a longer period long lasting than usual clouds, resulting in additional daylight currently being reflected back again to house.
“Solar local weather intervention“ is the umbrella time period for jobs this kind of as ours that involve reflecting daylight to minimize international warming and its most unsafe impacts. Other proposals consist of sprinkling reflective silicate beads around polar ice sheets and injecting elements with reflective properties, this kind of as sulfates or calcium carbonate, into the stratosphere. None of the approaches in this younger field are nicely comprehended, and they all have probably huge unidentified risks.
Solar local weather intervention is
not a replacement for cutting down greenhouse gasoline emissions, which is essential. But this kind of reductions would not deal with warming from current greenhouse gases that are previously in the environment. As the results of local weather improve intensify and tipping points are arrived at, we may will need alternatives to stop the most catastrophic penalties to ecosystems and human existence. And we’ll will need a very clear understanding of both of those the efficacy and risks of photo voltaic local weather intervention systems so men and women can make knowledgeable decisions about no matter if to apply them.
Our staff, dependent at the
College of Washington, the Palo Alto Investigate Heart (PARC), and the Pacific Northwest Nationwide Laboratory, comprises authorities in local weather modeling, aerosol-cloud interactions, fluid dynamics, and spray systems. We see a number of key rewards to marine cloud brightening around other proposed forms of photo voltaic local weather intervention. Working with seawater to crank out the particles offers us a absolutely free, plentiful source of environmentally benign materials, most of which would be returned to the ocean through deposition. Also, MCB could be completed from sea stage and would not rely on plane, so expenditures and affiliated emissions would be relatively low.
The results of particles on clouds are short-term and localized, so experiments on MCB could be carried out around smaller locations and temporary time intervals (it’s possible spraying for a handful of hrs for every day around a number of months or months) with out seriously perturbing the setting or international local weather. These smaller research would nevertheless produce substantial information on the impacts of brightening. What is additional, we can rapidly halt the use of MCB, with extremely swift cessation of its results.
Solar local weather intervention is the umbrella time period for jobs that involve reflecting daylight to minimize international warming and its most unsafe impacts.
Our task encompasses three important locations of investigate. Initial, we will need to find out if we can reliably and predictably improve reflectivity. To this finish, we’ll will need to quantify how the addition of created sea salt particles variations the quantity of droplets in these clouds, and analyze how clouds behave when they have additional droplets. Depending on atmospheric conditions, MCB could have an effect on matters like cloud droplet evaporation rate, the probability of precipitation, and cloud life span. Quantifying this kind of results will have to have both of those simulations and field experiments.
Next, we will need additional modeling to comprehend how MCB would have an effect on weather conditions and local weather both of those regionally and globally. It will be essential to analyze any destructive unintended penalties employing precise simulations right before everyone considers implementation. Our staff is initially concentrating on modeling how clouds respond to supplemental CCN. At some stage we’ll have to check out our function with smaller-scale field research, which will in convert improve the regional and international simulations we’ll operate to comprehend the possible impacts of MCB underneath diverse local weather improve eventualities.
The third important location of investigate is the growth of a spray technique that can deliver the dimension and focus of particles essential for the first smaller-scale field experiments. We’ll describe beneath how we’re tackling that obstacle.
Just one of the first actions in our task was to determine the clouds most amenable to brightening. By way of modeling and observational research, we decided that the greatest concentrate on is stratocumulus clouds, which are low altitude (all over one to 2 km) and shallow we’re notably interested in “thoroughly clean” stratocumulus, which have low quantities of CCN. The improve in cloud albedo with the addition of CCN is frequently solid in these clouds, whereas in further and additional remarkably convective clouds other procedures establish their brightness. Clouds around the ocean are likely to be thoroughly clean stratocumulus clouds, which is privileged, since brightening clouds around dim surfaces, this kind of as the ocean, will produce the greatest albedo improve. They are also conveniently near to the liquid we want to spray.
In the phenomenon named the Twomey impact, clouds with greater concentrations of smaller particles have a greater albedo, meaning they are additional reflective. Such clouds may possibly be less likely to deliver rain, and the retained cloud h2o would maintain albedo significant. On the other hand, if dry air from previously mentioned the cloud mixes in (entrainment), the cloud may deliver rain and have a decreased albedo. The complete impression of MCB will be the mixture of the Twomey impact and these cloud adjustments. Rob Wooden
Based on our cloud form, we can estimate the quantity of particles to crank out to see a measurable improve in albedo. Our calculation consists of the usual aerosol concentrations in thoroughly clean marine stratocumulus clouds and the improve in CCN focus essential to improve the cloud brightening impact, which we estimate at 300 to four hundred for every cubic centimeter. We also consider into account the dynamics of this section of the environment, named the marine boundary layer, looking at both of those the layer’s depth and the around three-day lifespan of particles in just it. Specified all all those factors, we estimate that a one spray technique would will need to constantly deliver roughly 3×10
fifteen particles for every second to a cloud layer that handles about 2,000 sq. kilometers. Because it really is likely that not each particle will attain the clouds, we must intention for an purchase or two better.
We can also establish the perfect particle dimension dependent on first cloud modeling research and performance factors. These research point out that the spray technique wants to crank out seawater droplets that will dry to salt crystals of just 30–100 nanometers in diameter. Any smaller than that and the particles will not act as CCN. Particles larger than a pair hundred nanometers are nevertheless productive, but their larger mass signifies that electrical power is wasted in generating them. And particles that are drastically larger than a number of hundred nanometers can have a destructive impact, considering that they can induce rainfall that outcomes in cloud loss.
We will need a very clear understanding of both of those the efficacy and risks of photo voltaic local weather intervention systems so men and women can make knowledgeable decisions about no matter if to apply them.
Making dry salt crystals of the exceptional dimension needs spraying seawater droplets of 120–400 nm in diameter, which is incredibly tricky to do in an electrical power-productive way. Regular spray nozzles, the place h2o is forced through a narrow orifice, deliver mists with diameters from tens of micrometers to a number of millimeters. To lower the droplet dimension by a variable of 10, the tension through the nozzle ought to improve additional than 2,000 times. Other atomizers, like the ultrasonic nebulizers uncovered in house humidifiers, in the same way can’t deliver smaller adequate droplets with out incredibly significant frequencies and power demands.
Solving this dilemma essential both of those out-of-the-box considering and experience in the generation of smaller particles. That is the place
Armand Neukermans came in.
Soon after a distinguished career at HP and Xerox targeted on generation of toner particles and ink jet printers, in 2009 Neukermans was approached by a number of eminent local weather experts, who requested him to convert his experience toward earning seawater droplets. He rapidly assembled a cadre of volunteers—mostly retired engineers and experts. and around the upcoming decade, these self-specified “Old Salts” tackled the obstacle. They worked in a borrowed Silicon Valley laboratory, employing gear scrounged from their garages or bought out of their have pockets. They explored a number of techniques of manufacturing the wished-for particle dimension distributions with several tradeoffs among particle dimension, electrical power performance, specialized complexity, dependability, and cost. In 2019 they moved into a lab house at PARC, the place they have accessibility to gear, elements, services, and additional experts with experience in aerosols, fluid dynamics, microfabrication, and electronics.
The three most promising strategies determined by the staff had been effervescent spray nozzles, spraying salt h2o underneath supercritical conditions, and electrospraying to form Taylor cones (which we’ll describe later on). The first selection was considered the least complicated to scale up rapidly, so the staff moved ahead with it. In an effervescent nozzle, pressurized air and salt h2o are pumped into a one channel, the place the air flows through the middle and the h2o swirls all over the sides. When the combination exits the nozzle, it produces droplets with measurements ranging from tens of nanometers to a handful of micrometers, with the mind-boggling quantity of particles in our wished-for dimension selection. Effervescent nozzles are made use of in a selection of apps, like engines, gasoline turbines, and spray coatings.
The key to this engineering lies in the compressibility of air. As a gasoline flows through a constricted house, its velocity increases as the ratio of the upstream to downstream pressures increases. This romantic relationship retains till the gasoline velocity reaches the pace of audio. As the compressed air leaves the nozzle at sonic speeds and enters the setting, which is at considerably decreased tension, the air undergoes a swift radial expansion that explodes the surrounding ring of h2o into tiny droplets.
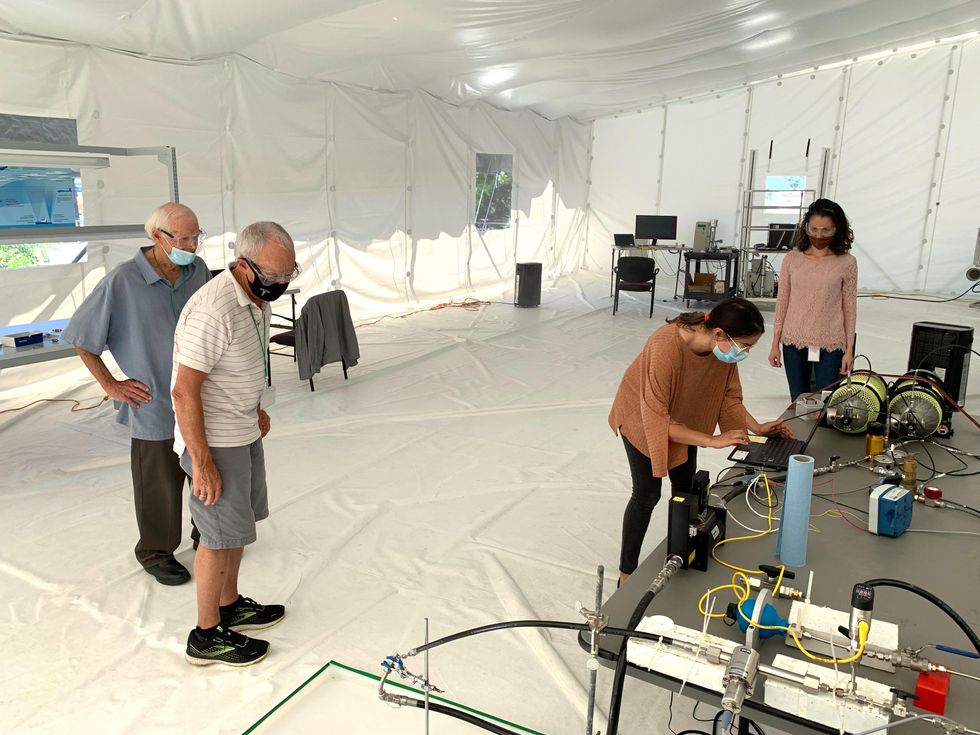
Coauthor Gary Cooper and intern Jessica Medrado take a look at the effervescent nozzle inside of the tent. Kate Murphy
Neukermans and company uncovered that the effervescent nozzle operates nicely adequate for smaller-scale testing, but the efficiency—the electrical power essential for every properly sized droplet—still wants to be improved. The two greatest sources of waste in our technique are the huge quantities of compressed air essential and the huge fraction of droplets that are as well significant. Our most up-to-date attempts have targeted on redesigning the flow paths in the nozzle to have to have smaller volumes of air. We’re also functioning to filter out the huge droplets that could induce rainfall. And to improve the distribution of droplet dimension, we’re looking at techniques to include demand to the droplets the repulsion among billed droplets would inhibit coalescence, decreasing the quantity of oversized droplets.
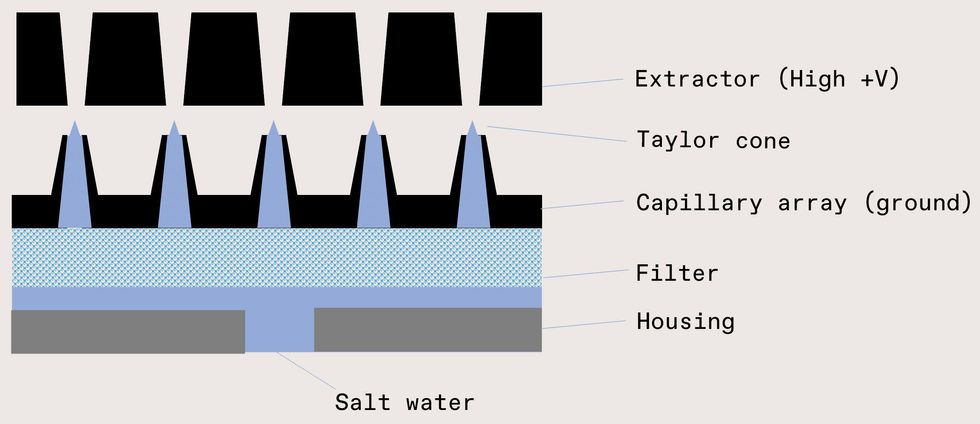
However we’re earning development with the effervescent nozzle, it hardly ever hurts to have a backup system. And so we’re also checking out electrospray engineering, which could produce a spray in which practically 100 % of the droplets are in just the wished-for dimension selection. In this approach, seawater is fed through an emitter—a narrow orifice or capillary—while an extractor makes a huge electric field. If the electrical power is of equivalent magnitude to the surface pressure of the h2o, the liquid deforms into a cone, ordinarily referred to as a Taylor cone. In excess of some threshold voltage, the cone idea emits a jet that rapidly breaks up into remarkably billed droplets. The droplets divide till they attain their Rayleigh limit, the stage the place demand repulsion balances the surface pressure. Fortuitously, surface seawater’s usual conductivity (four Siemens for every meter) and surface pressure (73 millinewtons for every meter) produce droplets in our wished-for dimension selection. The last droplet dimension can even be tuned by way of the electric field down to tens of nanometers, with a tighter dimension distribution than we get from mechanical nozzles.
This diagram (not to scale) depicts the electrospray technique, which takes advantage of an electric field to generate cones of h2o that crack up into tiny droplets. Kate Murphy
Electrospray is relatively simple to reveal with a one emitter-extractor pair, but a person emitter only produces 10
7–109 droplets for every second, whereas we will need 1016–1017 for every second. Developing that amount of money needs an array of up to 100,000 by 100,000 capillaries. Building this kind of an array is no smaller feat. We’re relying on strategies additional frequently affiliated with cloud computing than precise clouds. Working with the similar lithography, etch, and deposition strategies made use of to make integrated circuits, we can fabricate huge arrays of tiny capillaries with aligned extractors and specifically positioned electrodes.
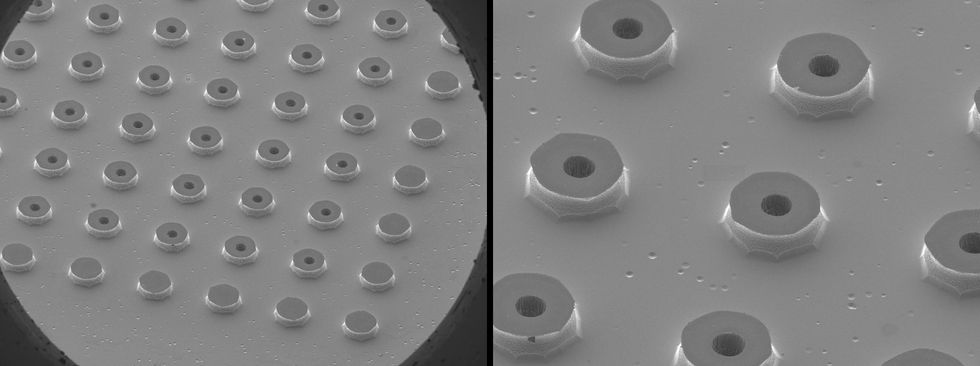
Visuals taken by a scanning electron microscope exhibit the capillary emitters made use of in the electrospray technique. Kate Murphy
Tests our systems provides nonetheless a further set of challenges. Ideally, we would like to know the first dimension distribution of the saltwater droplets. In exercise, which is virtually impossible to evaluate. Most of our droplets are smaller than the wavelength of gentle, precluding non-call measurements dependent on gentle scattering. As an alternative, we ought to evaluate particle measurements downstream, right after the plume has advanced. Our main resource, named a
scanning electrical mobility spectrometer, steps the mobility of billed dry particles in an electrical field to establish their diameter. But that strategy is delicate to factors like the room’s dimension and air currents and no matter if the particles collide with objects in the room.
To deal with these problems, we designed a sealed 425 cubic meter tent, outfitted with dehumidifiers, supporters, filters, and an array of connected sensors. Operating in the tent permits us to spray for for a longer period intervals of time and with several nozzles, with out the particle focus or humidity turning into greater than what we would see in the field. We can also analyze how the spray plumes from several nozzles interact and evolve around time. What is additional, we can additional specifically mimic conditions around the ocean and tune parameters this kind of as air pace and humidity.
Portion of the staff inside of the take a look at tent from remaining, “Old Salts” Lee Galbraith and Gary Cooper, Kate Murphy of PARC, and intern Jessica Medrado. Kate Murphy
We’ll inevitably outgrow the tent and have to shift to a huge indoor house to continue on our testing. The upcoming move will be outside testing to analyze plume behavior in actual conditions, even though not at a significant adequate rate that we would measurably perturb the clouds. We might like to evaluate particle dimension and concentrations much downstream of our sprayer, from hundreds of meters to a number of kilometers, to establish if the particles carry or sink and how much they distribute. Such experiments will aid us improve our engineering, answering this kind of thoughts as no matter if we will need to include warmth to our technique to stimulate the particles to rise to the cloud layer.
The details acquired in these preliminary assessments will also notify our products. And if the outcomes of the product research are promising, we can carry on to field experiments in which clouds are brightened sufficiently to analyze key procedures. As mentioned previously mentioned, this kind of experiments would be performed around a smaller and small time so that any results on local weather would not be substantial. These experiments would provide a important check out of our simulations, and as a result of our ability to properly predict the impacts of MCB.
It truly is nevertheless unclear no matter if MCB could aid modern society avoid the worst impacts of local weather improve, or no matter if it really is as well risky, or not productive adequate to be useful. At this stage, we don’t know adequate to advocate for its implementation, and we’re absolutely not suggesting it as an alternate to cutting down emissions. The intent of our investigate is to provide policymakers and modern society with the details essential to assess MCB as a person tactic to gradual warming, supplying information on both of those its possible and risks. To this finish, we’ve submitted our experimental options for evaluate by the
U.S. Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and for open up publication as section of a U.S. Nationwide Academy of Sciences analyze of investigate in the field of photo voltaic local weather intervention. We hope that we can shed gentle on the feasibility of MCB as a resource to make the planet safer.
From Your Site Articles or blog posts
Associated Articles or blog posts All-around the Web