The Search for Life on Mars Begins in February

On 18 February, the Mars2020 mission will touch down in a little crater named Jezero close to the Martian equator. The mission includes a rover named Perseverance that will explore the region, evaluate rocks and gather samples to be returned to Earth by a later mission owing to fly in 2026. The mission also includes a helicopter drone named Ingenuity that will scout in advance, searching for intriguing targets to examine.
Jezero is attention-grabbing since it was when crammed with liquid drinking water and so must contain important evidence of its effects. Even extra tantalizing is the probability that the crater when hosted lifestyle. In truth, portion of the Mars2020 mission is to research for indications of lifestyle and any biosignatures preserved in the rock.
Planetary geologists have very long examined Jezero, marking it as a prospective landing internet site for Mars missions. But the final decision to send out a rover there has manufactured it the goal of significantly extra examine.
In particular, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, presently orbiting the Red World, has despatched again several noticeable and infrared images of the area that have allowed geologists to examine remotely the kinds of rock Perseverance is probably to face.
Now Adrian Brown from NASA headquarters in Washington DC claims this operate has helped to generate a remarkably comprehensive image of the rocks that Perseverance will find and how they may have been altered by the motion of drinking water. Brown also discusses the thought that the rocks in Jezero crater are equivalent to Earth-bound outcrops in Warrawoona, Australia, which contain the oldest fossilized evidence of lifestyle on Earth.
Very first some track record. Mars was when incredibly diverse from the dry arid world we see currently. Some four billion years ago, Mars’s many volcanoes, some of the greatest in the Photo voltaic Process, commenced pumping enormous volumes of gasoline and dust into the ambiance.
This trapped vitality from the Sunlight leading to temperatures to rise and permitting liquid drinking water to pool on the surface area. The ambiance may even have supported clouds and rainfall, developing problems that were being ripe for the emergence of lifestyle.
But about three.7 billion years ago, the world commenced to awesome, together with its inside, shutting down the planet’s internal magnetic dynamo and destroying its magnetic area.
As the surface area cooled, the liquid drinking water froze at the poles or grew to become permafrost. This developed the problems for huge flooding. Each time an asteroid influence heated an region, the permafrost melted, sending torrents across the surface area. Currently, the world is scarred by the enormous channels carved by these floods.
Planetary geologists imagine Jezero crater crammed with drinking water at minimum twice but that the resulting lakes were being very long lived, long lasting maybe 10 million years and eventually disappearing about three.7 billion years ago. “This may possibly be the closing time drinking water flowed on Mars,” claims Brown, who presented this paper at the 23rd Worldwide Mars Culture Conference in October.
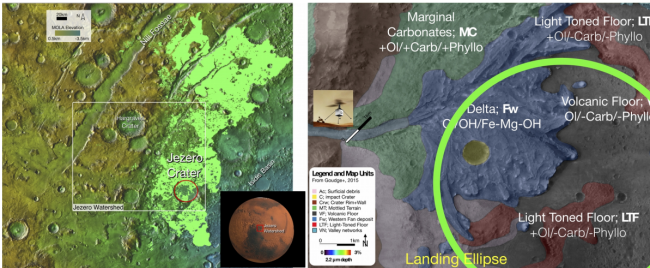
The crater is about fifty kilometers in diameter and properly-examined employing the cameras aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The images at many frequencies of noticeable and infrared light reveal the composition of the rock and also its grain measurement, which reveals how it has weathered about time.
Brown claims this shows the crater was originally fashioned in rock consisting of olivine, a mineral that contains iron, magnesium and silicates, as properly as properly carbonates. Brown claims an critical discovery is a rocky outcrop beyond the waterline that reveals the unaltered rock as it originally fashioned. This will develop into an essential reference for the mission, versus which altered rocks can be in comparison.
Drinking water Will work
Within the crater, clay has fashioned in many spots, which geologists feel can only occur in the presence of drinking water, which will have carried the necessary minerals from bordering spots. This is probably to have fashioned in levels, which may possibly be noticeable close to the shoreline.
The most intriguing line of investigation is Brown’s comparison among the rocks in Jezero crater and individuals at Warrawoona in Australia. Back again in 1983, paleobiologists uncovered evidence of fossilized cells in these rocks, which fashioned some three.five billion years ago. They depict the oldest geological evidence of lifestyle on Earth.
That right away raises the tantalizing probability that equivalent evidence may be current in Jezero crater. If so, an critical question is irrespective of whether Perseverance will be capable to gather this evidence and evaluate it in the necessary detail.
That is a significant check with, even for a mission created to glimpse for indications of lifestyle. “The limitations in spaceflight-prepared instrumentation and the remote spot of the scientific crew limit the extent of scientific analyses that can be carried out by rover missions to Mars,” Brown details out.
But even if not, Perseverance will gather samples that will later be returned to Earth by a sample return mission. The gain of such an approach is that the rocks can be examined in extra detail by a wider wide range of instruments. “Inspired by the Apollo samples, which even now continue propel new lunar science discoveries, we anticipate that the analyses of the samples returned by MSR will depend on potential instrumentation that may possibly not even exist currently,” claims Brown.
Brown claims NASA and the European Place Agency have agreed to operate on the sample return mission with each other. “The nominal start date is planned for 2026, with a nominal return of samples by 2031,” he claims. So for a definitive reply to any concerns about indications of lifestyle on Mars, we will almost certainly have to wait around right until then.
Ref: Mars2020 and Mars Sample Return arxiv.org/abs/2012.08946







