Carbon-Removal Tech Grabs Elon Musk’s Check
A lot of persons are hungry for answers to these issues—witness the widespread adoption in excess of the previous 10 years of wireless charging, mostly for transportable purchaser electronics but
also for cars. Whilst a wi-fi charger saves you from owning to join and disconnect cables repeatedly, the length over which electricity can be delivered this way is rather short. Without a doubt, it is tricky to recharge or energy a system when the air gap is just a several centimeters, a great deal considerably less a handful of meters. Is there truly no sensible way to send out electricity more than better distances with no wires?
To some, the full idea of wireless electrical power transmission evokes photographs of Nikola Tesla with substantial-voltage coils spewing miniature bolts of lightning. This wouldn’t be these kinds of a foolish connection to make. Tesla had in fact pursued the concept of by some means utilizing the floor and atmosphere as a conduit for extended-length electricity transmission, a approach that went nowhere. But his dream of sending electrical electricity over good distances with no wires has persisted.
To underscore how risk-free the method was, the host of the BBC science program “Bang Goes the Theory” caught his face completely into a power beam.
Guglielmo Marconi, who was Tesla’s modern day, figured out how to use “Hertzian waves,” or electromagnetic waves, as we connect with them right now, to deliver alerts more than extensive distances. And that advance introduced with it the probability of applying the same form of waves to carry strength from 1 put to a different. This is, right after all, how all the strength stored in wooden, coal, oil, and natural fuel at first got in this article: It was transmitted 150 million kilometers by means of area as electromagnetic waves—sunlight—most of it tens of millions of decades ago.
Can the exact basic physics be harnessed to substitute wires nowadays? My colleagues and I at the U.S.
Naval Exploration Laboratory, in Washington, D.C., think so, and listed here are some of the causes why.
There have been sporadic endeavours above the earlier century to use electromagnetic waves as a implies of wireless electrical power transmission, but these makes an attempt generated mixed benefits. Most likely the golden calendar year for analysis on wi-fi energy transmission was 1975, when William Brown, who worked for
Raytheon, and Richard Dickinson of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (now retired) used microwaves to beam electricity throughout a lab with greater than 50 percent conclude-to-close effectiveness. In a different demonstration, they ended up in a position to supply much more than 30 kilowatts above a distance of about a mile (1.6 kilometers).
These demonstrations have been aspect of a bigger NASA and
U.S. Section of Electrical power campaign to explore the feasibility of photo voltaic-electric power satellites, which, it was proposed, would 1 day harvest daylight in place and beam the power down to Earth as microwaves. But mainly because this line of research was inspired in substantial section by the vitality disaster of the 1970s, curiosity in photo voltaic-ability satellites waned in the pursuing a long time, at minimum in the United States.
Even though scientists revisit the notion of solar-energy satellites with some regularity, all those performing true demonstrations of electrical power beaming have struggled to surpass the higher-water mark for performance, length, and electric power degree attained in 1975. But that predicament is commencing to change, many thanks to various modern advances in transmission and reception technologies.
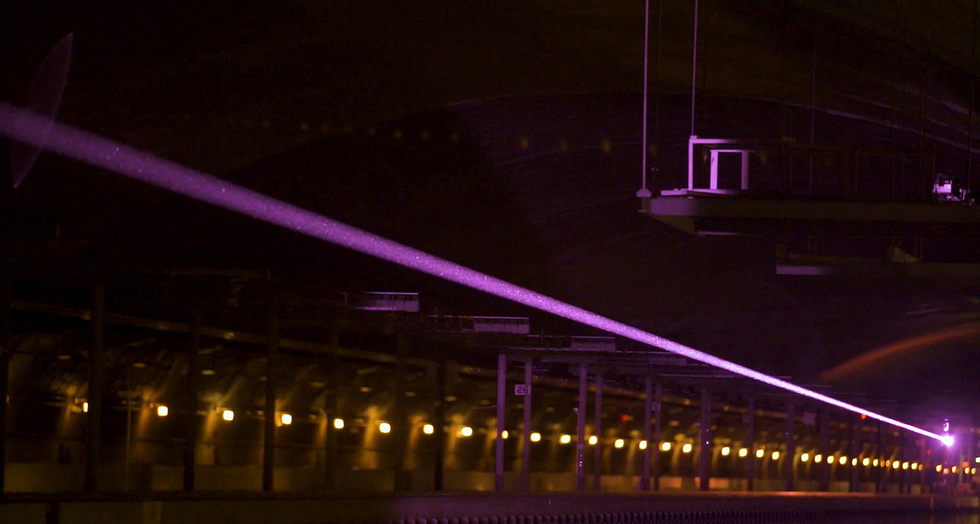

In the course of a 2019 demonstration at the Naval Surface Warfare Middle in Bethesda, Md., this laser beam safely conveyed 400 watts above a distance of 325 meters.U.S. Naval Investigation Laboratory
Most early endeavours to beam electrical power were being confined to microwave frequencies, the exact same portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that today teems with Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and a variety of other wireless signals. That selection was, in section, driven by the simple point that productive microwave transmitting and getting products was conveniently accessible.
But there have been advancements in performance and elevated availability of products that operate at significantly bigger frequencies. Due to the fact of limitations imposed by the environment on the productive transmission of strength in specified sections of the electromagnetic spectrum, scientists have concentrated on microwave, millimeter-wave, and optical frequencies. Whilst microwave frequencies have a slight edge when it comes to efficiency, they have to have larger sized antennas. So, for many applications, millimeter-wave or optical hyperlinks get the job done superior.
For programs that use microwaves and millimeter waves, the transmitters usually make use of good-condition digital amplifiers and phased-array, parabolic, or metamaterial antennas. The receiver for microwaves or millimeter waves makes use of an array of aspects identified as rectennas. This word, a portmanteau of
rectifier and antenna, reflects how each individual element converts the electromagnetic waves into direct-present electrical power.
Any process intended for optical electric power transmission would possible use a laser—one with a tightly confined beam, this kind of as a fiber laser. The receivers for optical electrical power transmission are specialised photovoltaic cells made to convert a single wavelength of light-weight into electric powered ability with quite significant performance. Certainly, efficiencies can exceed 70 percent, additional than double that of a typical solar cell.
At the U.S. Naval Study Laboratory, we have invested the greater element of the earlier 15 many years on the lookout into diverse choices for electricity beaming and investigating likely apps. These consist of extending the flight instances and payload capacities of drones, powering satellites in orbit when they are in darkness, powering rovers running in permanently shadowed regions of the moon, sending electricity to Earth’s surface from place, and distributing strength to troops on the battlefield.
You may well consider that a system for sending large amounts of electrical power through the air in a narrow beam seems like a dying ray. This receives to the heart of a essential consideration: electrical power density. Distinctive electricity densities are technically possible, ranging from far too reduced to be helpful to high sufficient to be hazardous. But it’s also probable to find a pleased medium involving these two extremes. And there are also clever ways to allow beams with higher energy densities to be employed safely and securely. Which is just what a crew I was component of did in 2019, and we’ve correctly extended this get the job done considering that then.
A person of our field companions,
PowerLight Systems, formerly known as LaserMotive, has been producing laser-primarily based energy-beaming systems for far more than a decade. Renowned for winning the NASA Electrical power Beaming Problem in 2009, this business has not only accomplished achievements in powering robotic tether climbers, quadcopters, and set-wing drones, but it has also delved deeply into the challenges of safely beaming energy with lasers. That is important, for the reason that lots of investigation groups have shown laser power beaming more than the years—including groups at the Naval Investigation Laboratory, Kindai University, the Beijing Institute of Know-how, the College of Colorado Boulder, JAXA, Airbus, and others—but only a handful of have achieved it in a manner that is certainly safe less than every single plausible circumstance.
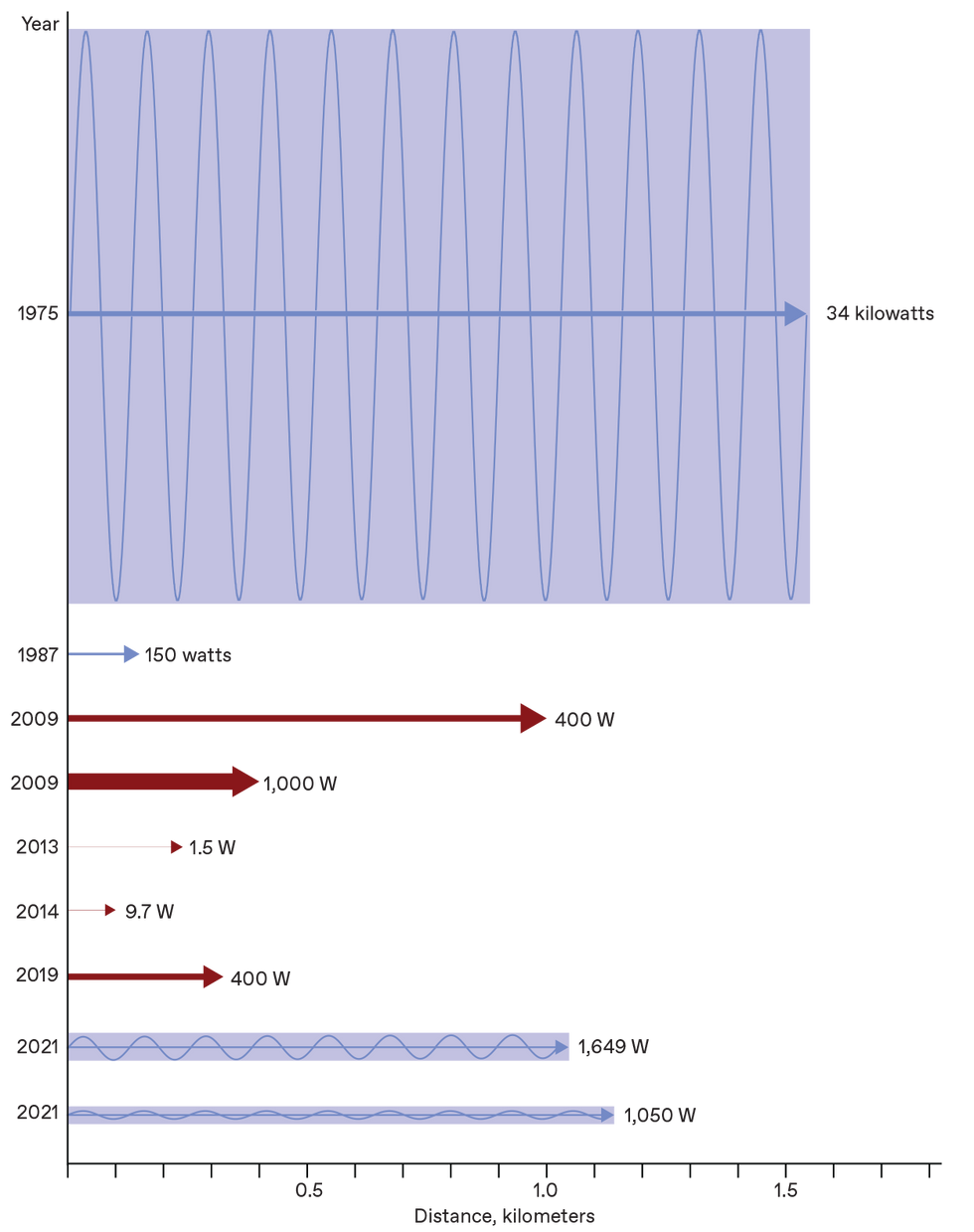
There have been many demonstrations of power beaming around the a long time, using both microwaves [blue] or lasers [red], with the peak-electrical power document acquiring been set in 1975 [top]. In 2021, the writer and his colleagues took next and 3rd area for the peak-power stage attained in these types of experiments, having beamed additional than a kilowatt more than distances that exceeded a kilometer, utilizing considerably smaller sized antennas.
David Schneider
Perhaps the most extraordinary demonstration of risk-free laser energy beaming prior to our team’s effort and hard work was by the corporation
Lighthouse Dev in 2012. To underscore how risk-free the technique was, the host of the BBC science software “Bang Goes the Theory” caught his face thoroughly into a electrical power beam despatched in between buildings at the College of Maryland. This distinct demonstration took gain of the fact that some infrared wavelengths are an get of magnitude safer for your eyes than other pieces of the infrared spectrum.
That strategy operates for rather lower-ability methods. But as you press the stage greater, you shortly get to ability densities that increase safety considerations no matter of the wavelength utilised. What then? Here’s where the method we have demonstrated sets itself aside. Even though sending a lot more than 400 watts about a distance that exceeded 300 meters, the beam was contained within just a virtual enclosure, one that could feeling an object impinging on it and induce the machines to minimize electricity to the main beam prior to any damage was carried out. Other testing has proven how transmission distances can exceed a kilometer.
Very careful tests (for which no BBC science-software hosts were utilised) verified to our satisfaction the performance of this feature, which also passed muster with the Navy’s Laser Basic safety Assessment Board. Through the class of our demonstration, the process even further proved itself when, on numerous occasions, birds flew towards the beam, shutting it off—but only momentarily. You see, the process screens the quantity the beam occupies, along with its rapid surroundings, allowing for the electrical power link to quickly reestablish alone when the route is once once again very clear. Think of it as a much more refined version of a garage-doorway basic safety sensor, where the interruption of a guard beam triggers the motor driving the door to shut off.
The 400 watts we had been in a position to transmit was, admittedly, not a enormous sum, but it was adequate to brew us some coffee.
For our demonstrations, observers in attendance were capable to walk all-around involving the transmitter and receiver without having needing to use laser-basic safety eyewear or consider any other safety measures. That is simply because, in addition to creating the system so that it can shut alone down immediately, we took care to consider the possible results of reflections from the receiver or the scattering of gentle from particles suspended in the air along the route of the beam.
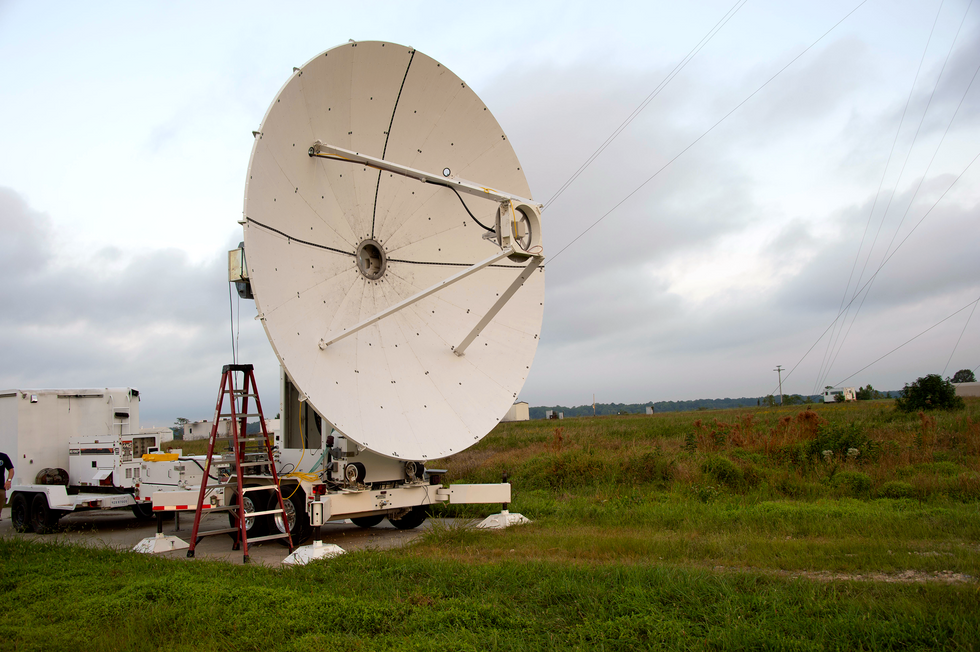
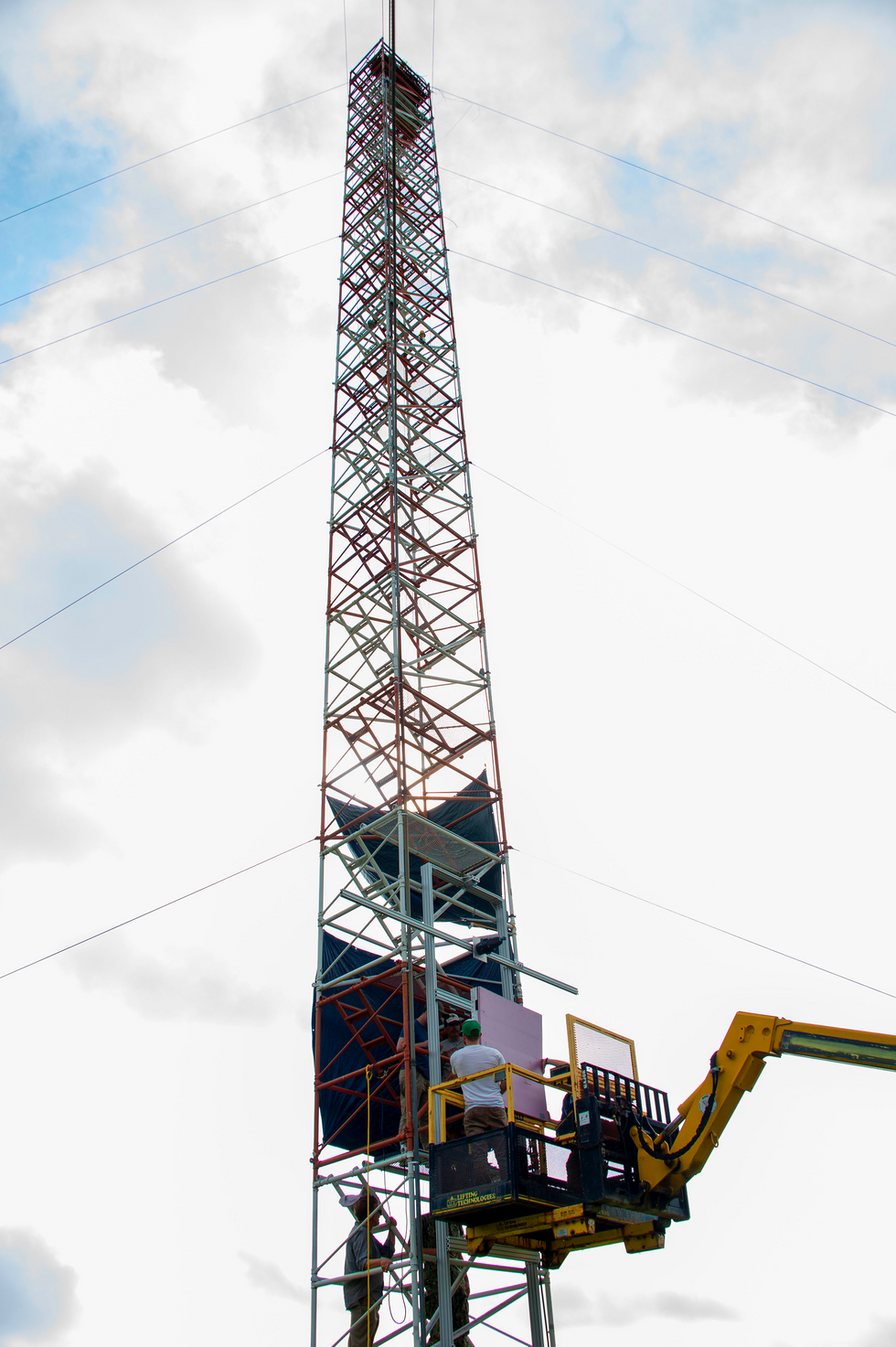

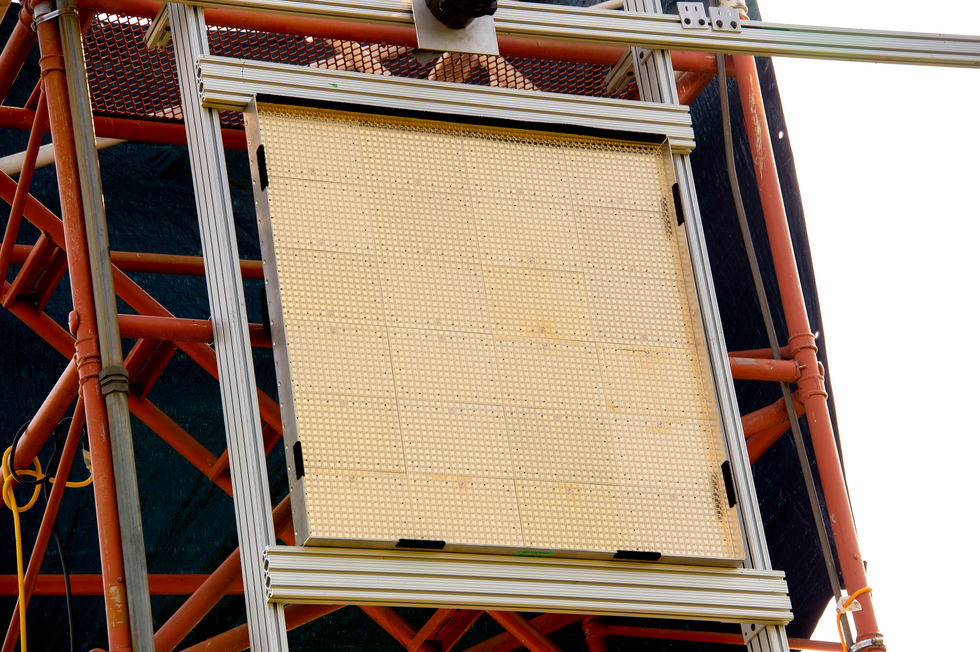

Final calendar year, the author and his colleagues carried out a demonstration at the U.S. Army’s Blossom Point take a look at facility south of Washington, D.C. They utilised 9.7-gigahertz microwaves to ship 1,649 watts (peak power) from a transmitter outfitted with a 5.4-meter diameter parabolic dish [top] more than a distance of 1,046 meters to a 2-by-2-meter “rectenna” [middle] mounted on a tower [bottom], which reworked the beam into usable electrical energy.U.S. Naval Research Laboratory
The 400 watts we ended up ready to transmit was, admittedly, not a enormous total, but it was adequate to brew us some coffee, continuing what’s come to be de rigueur in this line of experimentation: producing a incredibly hot beverage. (The Japanese researchers who commenced this custom in 2015 geared up by themselves some tea.)
Our subsequent purpose is to apply electricity beaming, with entirely integrated security measures, to cellular platforms. For that, we assume to boost the length coated and the quantity of electrical power sent.
But we’re not alone: Other governments, proven providers, and startups around the globe are functioning to produce their own ability-beaming methods. Japan has lengthy been a chief in microwave and laser power beaming, and China has shut the hole if not pulled forward, as has South Korea.
At the customer-electronics degree, there are lots of gamers:
Powercast, Ossia, Energous, Guru, and Wi-Cost amid them. And the multinational engineering huge Huawei expects energy beaming for smartphone charging in “two or a few [phone] generations.”
For industrial apps, organizations like
Attain Labs, TransferFi, MH GoPower, and MetaPower are generating headway in using electric power beaming to resolve the thorny issue of trying to keep batteries for robots and sensors, in warehouses and elsewhere, topped off and completely ready to go. At the grid amount, Emrod and other individuals are trying to scale power beaming to new heights.
On the R&D front, our crew shown inside of the previous calendar year safe and sound microwave wi-fi electrical power transmission of
1.6 kilowatts around a length of a kilometer. Businesses like II-VI Aerospace & Defense, Peraton Labs, Lighthouse Dev, and other folks have also not too long ago designed outstanding strides. These days, bold startups like Solar House Technologies, Solaren, Virtus Solis, and other people working in stealth method are doing the job tough to be the first to attain functional ability beaming from place to Earth.
As these types of organizations build confirmed keep track of information for protection and make persuasive arguments for the utility of their systems, we are possible to see whole new architectures emerge for sending energy from put to put. Imagine drones that can fly for indefinite durations and electrical gadgets that by no means need to have to be plugged in—ever—and becoming able to provide individuals any where in the environment with strength when hurricanes or other natural disasters ravage the neighborhood electric power grid. Lowering the need to have to transportation gas, batteries, or other kinds of stored energy will have much-achieving implications. It is not the only alternative when you simply cannot string wires, but my colleagues and I hope, in the established of doable systems for furnishing electrical energy to far-flung places, that electric power beaming will, pretty actually, shine.
This article appears in the June 2022 print situation as “Spooky Electrical power at a Length.”
From Your Web-site Content articles
Associated Posts About the Internet







